The single-step format is useful for getting a snapshot of your company’s profitability, and not much else, which is why it’s not as common as the multi-step income statement. But if you’re looking for a super simple financial report to calculate your company’s financial performance, single-step is the way to go. A trial balance is a statement of all the ledger account balances at a specific point in time. On the other hand, an income statement is a financial statement that reports revenues and expenses over a period of time; it also shows the net income or loss for the period.

While an income statement displays a company’s financial performance over a specific period (e.g. a quarter or a year), a balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a given moment in time. The balance sheet consists of assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity, revealing what the company owns, what it owes, and the equity owned by shareholders. Depreciation is an accounting method that allows companies to allocate the cost of tangible assets, such as machinery, vehicles, and equipment, over their useful life.
The Difference Between Single-Step and Multi-Step
A projected income statement can be prepared from past sales and expenses, especially by established businesses. Therefore, a comparative income statement can give a trend of income and expenses of the company, to know whether income is increasing or not; and also shows whether the loss is increasing or not. Preparing income statements helps investors to make a choice on which business is best to invest in it. A company that meets its goals or exceeds its targets would be preferred by investors over one that always misses the targets. An income statement is also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), a profit and loss account, or a statement of profit or loss. Non-operating expenses, on the other hand, refer to costs incurred but not linked directly to the core functions of a business.
The operating expenses section contains a number of line items that may instead be classified as selling, general and administrative expenses. It includes all expenses required to run the business that were not already included in the cost of goods sold. These expenses cover the areas of sales, marketing, IT, risk management, human resources, accounting, and finance. The line items in this section may be stated by function, such as rent expense, utilities expense, and compensation expense. While not present in all income statements, EBITDA stands for Earnings before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is calculated by subtracting SG&A expenses (excluding amortization and depreciation) from gross profit.
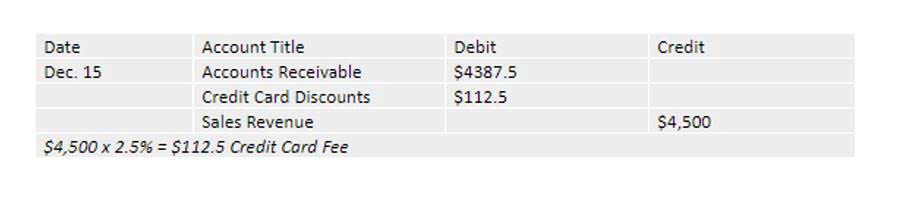
Partial income statement
The Income Statement, also called “Profit and Loss Statement”, summarizes the financial performance or results of operations of a business for a particular period of time. The income statement reflects all the incomes, expenses, profits, and losses in a company, which we put into mathematical equations to reach the net profit or loss for that accounting period. A high operating profit margin indicates that a company is efficient and has good control over its costs. Conversely, a low operating profit margin indicates that a company needs to improve its efficiency and/or reduce its operating expenses. The net income on the income statement is the amount of money that remains after all taxes and expenses have been deducted from the revenue. It represents the amount that is free to be used when the taxes have been paid and all the expenses have been deducted.
There is no gross profit subtotal, as the cost of sales is grouped with all other expenses, which include fulfillment, marketing, technology, content, general and administration (G&A), and other expenses. The first section, titled Revenue, indicates that Microsoft’s gross which accounts are found on an income statement (annual) profit, or gross margin, for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2021, was $115.86 billion. It was arrived at by deducting the cost of revenue ($52.23 billion) from the total revenue ($168.09 billion) realized by the technology giant during this fiscal year.
Depreciation
The purpose of an income statement is to show a company’s financial performance over a given time period. Also known as profit and loss (P&L) statements, income statements summarize all income and expenses over a given period, including the cumulative impact of revenue, gain, expense, and loss transactions. Income statements are often shared as quarterly and annual reports, showing financial trends and comparisons over time. It’s important to note that there are several different types of income statements that are created for different reasons. For example, the year-end statement that is prepared annually for stockholders and potential investors doesn’t do much good for management while they are trying to run the company throughout the year.
By understanding the income and expense components of the statement, an investor can appreciate what makes a company profitable. Though calculations involve simple additions and subtractions, the order in which the various entries appear in the statement and their relationships often get repetitive and complicated. The link between an income statement and a balance sheet is that both are financial statements that show the financial health of a company. The two statements are interconnected because the net income from the income statement becomes part of the equity on the balance sheet.
